9
Marzo
2012.
Volumen
11
-
N
°
48
iniciando por los factores clínicos, luego por los
hallazgos del laboratorio y finalmente las
patologías asociadas; estos son: peso al ingreso
<
2700
g, sepsis e incompatiblidad Rh.
En resumen, los factores de riesgo son
predictores útiles de encefalopatía bilirrubínica
aguda y crónica cuando los niveles de
bilirrubinemia sérica total están sobre los
25
mg/dL y los principales son: el peso al
ingreso <
2700
g, sepsis e incompatibilidad Rh.
Cuando estos factores no están presentes
el riesgo de desarrollar ABE y BE es
significativo si el nivel de bilirrubina sérica
total sobrepasa los
30
mg/dL.
Referencias:
1.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Subcommittee on Neonatal Hyperbilirrubinemia. Clinical practice guideline: Management of
hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant
35
or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics.
2004;114(1):297-316.
2.
Ogunlesi TA, Dedeke IO, Adekanmbi AF, Fetuga MB, Ogunfowora OB. The incidence and outcome of bilirubin encephalopathy in
Nigeria: a bi-centre study. Niger J Med.
2007
Oct-Dec;
16(4):354-9.
3.
Gamaleldin R, Iskander I, Seoud I, Aboraya H, Aravkin A, Sampson PD, Wennberg RP. Risk Factors for Neurotoxicity in Newborns With
Severe Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics.
2011
Oct;
128(4):E925-31.
4.
Newman TB, Liljestrand P, Jeremy RJ, Ferriero DM, Wu YW, Hudes ES, Escobar GJ; Jaundice and Infant Feeding Study Team. Outcomes
among newborns with total serum bilirubin levels of
25
mg per deciliter or more. N Engl J Med.
2006
May
4;354(18):1889-900.
5.
Newman TB, Liljestrand P, Escobar GJ. Infants with bilirubin levels of
30
mg/dL or more in a large managed care organization.
Pediatrics.
2003;111(6
pt
1):1303–1311.
6.
Ogunlesi TA, Ogunfowora OB. Predictors of acute bilirubin encephalopathy among Nigerian term babies with moderate-to-severe
hyperbilirubinaemia. J Trop Pediatr.
2011
Apr;
57(2):80-6
. Epub
2010
Jun
15
.
7.
Wennberg RP, Ahlfors CE, Aravkin AY. Intervention guidelines for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: an evidence based quagmire. Curr
Pharm Des.
2009;15(25):2939-45.
Revisado por Dra. Sofía Aros A. Neonatóloga, Hospital Clínico San Borja Arriarán.
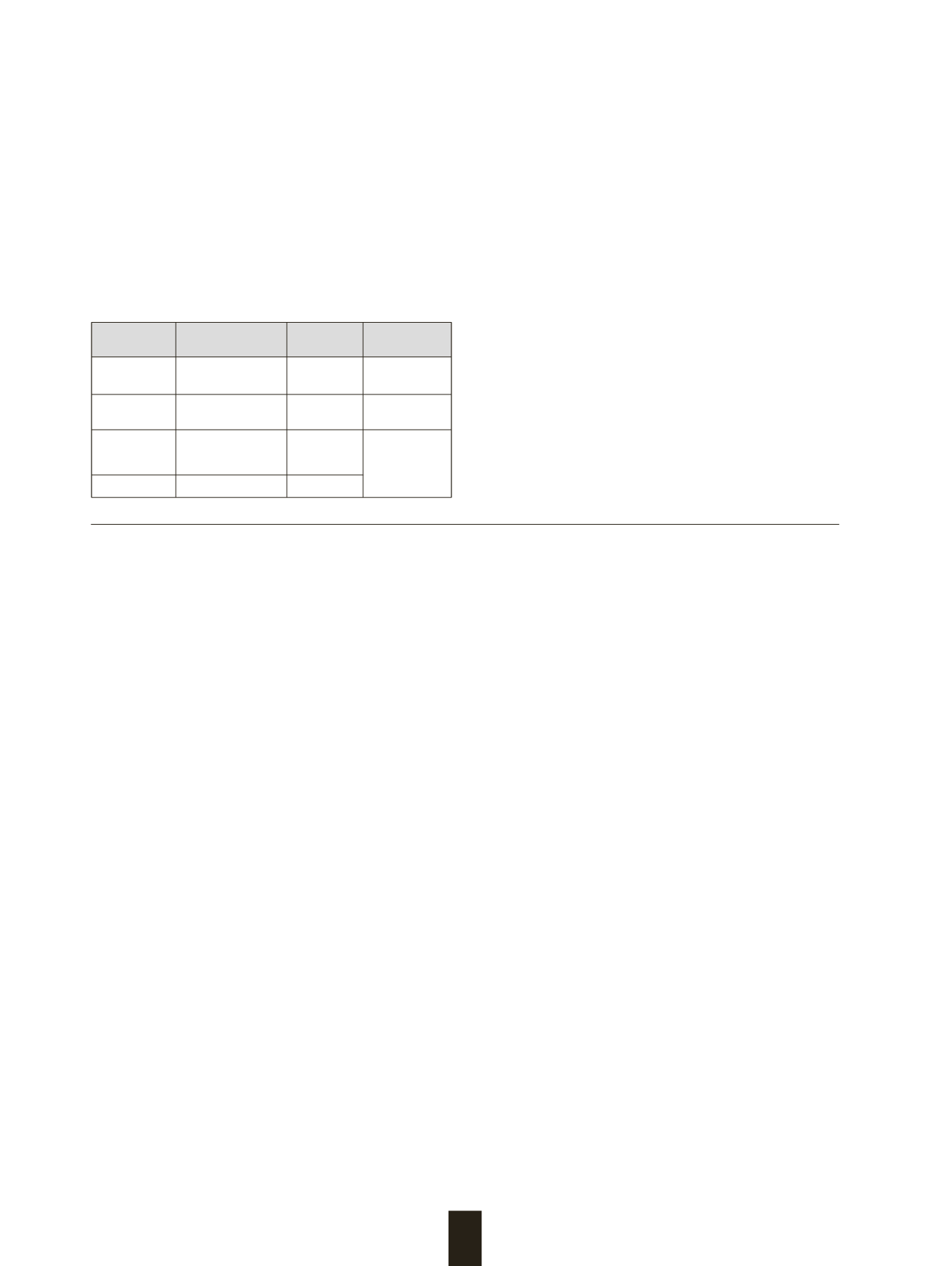
Tabla
4
. Factores de riesgo para desarrollar encefalopatía
bilirrubínica en neonatos con hiperbilirrubinemia
≥
25
mg/dL.
Examen Físico
Peso al ingreso
<
2700
g
Signos de sepsis
Letargia significativa
Inestabilidad térmica
Antecedentes
Parto no
institucional
Bajo nivel
socioeconómico
Prematurez
Bajo nivel
educacional
de la madre
Acidosis
metabólica
Anemia
severa
Hallazgos
al Laboratorio
Incompatibilidad
Rh y ABO
Sepsis
Déficit de la
glucosa-
6
-fosfato
deshidrogenasa
Patologías
Asociadas